What Kinda Mitosis Mutations Could Happen When a Baby Is Born
Chromosomal Mutations: In living organisms, mutations occur at a charge per unit of one per every ten one thousand thousand cell replications. And as compared to the more than 100 trillion cells in the human body, this number is rather insignificant.
Chromosomes are thread-similar structures where the genetic material Deoxyribonucleic acid is packaged. They are located in the nucleus of cells and undergo condensation before cell division. Like any other processes, the chromosome may run into random genetic changes or be affected by it.
On this folio, we explored what happens when a chromosome encounters such changes in its structure, number, and blazon.
Table of Contents
- What is a Chromosomal Mutation?
- Structural Chromosomal Mutations
- 1. Deletion
- Disorders Due To Deletion
- 2. Duplication
- Disorders Due To Duplication
- 3. inversion
- Disorders Due To Inversion
- 4. Translocation
- Disorders Due To Translocation
- 1. Deletion
- Chromosomal Number Mutations
- 1. Aneuploidy
- two. Polyploidy
- The Advantages of Chromosomal Mutations
- ane. Survival
- 2. Diversity
- The Disadvantages of Chromosomal Mutations
- 1. Genetic Disorder
- 2. Other Diseases
- Cite This Page
What is a Chromosomal Mutation?
 Past definition, a chromosomal mutation is whatsoever modify or error that occurs inside the chromosome. Such errors can exist attributed to any mistakes or problems that occur during cell processes similar mitosis and meiosis.
Past definition, a chromosomal mutation is whatsoever modify or error that occurs inside the chromosome. Such errors can exist attributed to any mistakes or problems that occur during cell processes similar mitosis and meiosis.
- Unlike gene mutations that involve the alteration of a gene or a segment of DNA in the chromosome, chromosomal mutations occur and change the entirety of the chromosome itself.
- Iii types of chromosomal mutations exist: mutations on the construction of chromosomes, mutations on the chromosome number, and mutations on the sex chromosomes.
![]()
Structural Chromosomal Mutations
This kind of chromosomal mutation usually occurs during any errors in cell sectionalisation. This happens when homologous chromosomes paired upward, genes in chromosomes broke apart, genes inserted in the wrong chromosome, or genes or set of genes are completely lost in the chromosome.
Basically, structural chromosomal mutations are classified into 4: deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation (or shift places). They are illustrated below:
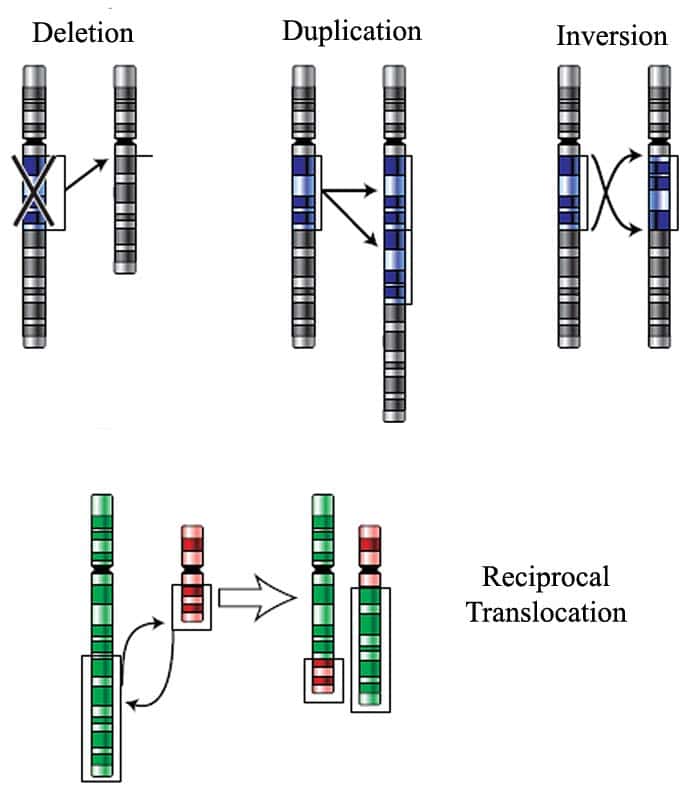
1. Deletion
This type of mutation occurs when a role of the Deoxyribonucleic acid is non duplicated or is lost during DNA replication. The size of this region can either be a mere nucleotide or tin can exist large every bit an unabridged chromosome.
Disorders Due To Deletion
Common disorders due to deletion mutation in humans are: Cri du chat, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Di George'south syndrome, etc.
![]()
2. Duplication
This type of mutation occurs when an extra copy of a region (or regions) in the Deoxyribonucleic acid is produced. This duplicated region can either be located in its normal location in the chromosome or sometimes exist located in other parts of the chromosomes or even in another chromosome.
- This duplication tin can now supply additional textile that has the ability to evolve new functions.
Disorders Due To Duplication
Mutual disorder due to duplication mutation in humans is: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type I.
![]()
3. inversion
During inversion, a portion in the chromosome is reversed and gets inserted dorsum into the chromosome. Basically, 2 types of inversion be: pericentric and paracentric.
- During a pericentric inversion, the inversion encompasses the centromere What is Centremere?The Centromere is a constriction in a chromosome; at one point along its length dividing information technology into a shorter arm, called the p arm, and a longer arm, called the q arm. of the chromosome.
- On the other manus, during a paracentric inversion, information technology but involves either the short or long arm of the chromosome and the inversion signal does not include the centromere.
Disorders Due To Inversion
Common disorder due to inversion mutation in humans is: Amniocentensis during pregnancy.
![]()
4. Translocation
Translocation happens when a fragmented chromosome tends to bring together with a nonhomologous chromosome. This newly-formed segment so detaches from the chromosome and moves to a new position on another chromosome.
Disorders Due To Translocation
Common disorders due to translocation mutation in humans are: Xx male syndrome, Downward syndrome, Infertility and Cancer.
![]()
Chromosomal Number Mutations
ane. Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is a type of mutation in the chromosome number wherein the ploidy (chromosome number) of the new individual is different from its wild type. This is typically a result of the nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis, hence producing offspring with either extra or lost chromosomes.
- The naming of aneuploid weather is more often than not based on the number of chromosomes added or deleted. For instance, a monosomic (2n -one) individual bears only i copy of a chromosome, instead of having two.
- Other variations of aneuploidy are trisomic (2n+1), nullisomic (2n-2), and disomic (n+one).
![]()
2. Polyploidy
Polyploidy is a type of mutation that occurs when an individual bears more than one haploid ready of chromosomes. If the private with polyploidy deport three sets of haploid chromosomes, the condition is said to exist triploidy whereas if it has four haploid sets, the condition is said to be tetraploidy.
- Interestingly, polyploidy is a common phenomenon amongst plants as well as sure groups of fish, salamanders, frogs, and leeches.
![]()
The Advantages of Chromosomal Mutations
Believe it or not, the random errors that occur during cell division can be beneficial for organisms. Listed beneath are some of them.
ane. Survival
Mutations are very essential for populations considering they aid some individuals of the population to arrange to their surroundings while they maintain their survival. They are also an of import strength in evolution because they residual out the frequency of alleles nowadays in the population.
- In humans, some successful mutations include malaria resistance, lactose tolerance, and atherosclerosis tolerance.
![]()
ii. Diversity
Mutations in the chromosomes is highly connected to diversity (not only genetically but also physically) of living organisms. Ultimately, the close interactions between inherited mutations and environmental pressures generate diversity amongst species.
- And clearly, without genetic multifariousness, some of the fundamental mechanisms of evolutionary change cannot (and continue to) operate.
- Examples: As some chromosomal mutations are harmless, humans become different color eyes such as black, brown, gray, greenish or blue.
![]()
The Disadvantages of Chromosomal Mutations
Some mutations tin be quite detrimental as well. The post-obit are the some of the near mutual disadvantages of mutations in the chromosomes:
1. Genetic Disorder
Mutations in the chromosome can cause a wide diversity of genetic disorders. While most genetic disorders are rare, the severity of the error in even a pocket-sized portion of the chromosome tin can be highly devastating.
![]()
2. Other Diseases
Aside from inheritable disorder, certain mutations in the chromosomes can besides bring about the onset of other diseases like cancer (i.e. lung, breast, and float.).
![]()
No affair what we do, the random changes in our genome are highly inevitable. And in this case, does the saying "the merely constant is alter" prove true?
Cite This Page
Source: https://www.bioexplorer.net/chromosomal-mutations.html/
0 Response to "What Kinda Mitosis Mutations Could Happen When a Baby Is Born"
Post a Comment